模板语法 | Template Refs
Vue uses an HTML-based template syntax that allows you to declaratively bind the rendered DOM to the underlying component instance's data. All Vue templates are syntactically valid HTML that can be parsed by spec-compliant browsers and HTML parsers.
Vue 使用一种基于 HTML 的模板语法,使我们能够声明式地将其组件实例的数据绑定到呈现的 DOM 上。所有的 Vue 模板都是语法层面合法的 HTML,可以被符合规范的浏览器和 HTML 解析器解析。
Under the hood, Vue compiles the templates into highly-optimized JavaScript code. Combined with the reactivity system, Vue can intelligently figure out the minimal number of components to re-render and apply the minimal amount of DOM manipulations when the app state changes.
在底层机制中,Vue 会将模板编译成高度优化的 JavaScript 代码。结合响应式系统,当应用状态变更时,Vue 能够智能地推导出需要重新渲染的组件的最少数量,并应用最少的 DOM 操作。
If you are familiar with Virtual DOM concepts and prefer the raw power of JavaScript, you can also directly write render functions instead of templates, with optional JSX support. However, do note that they do not enjoy the same level of compile-time optimizations as templates.
如果你对虚拟 DOM 的概念比较熟悉,并且偏好直接使用 JavaScript,你也可以结合可选的 JSX 支持直接手写渲染函数而不采用模板。但请注意,这将不会享受到和模板同等级别的编译时优化。
文本插值 | Text Interpolation
The most basic form of data binding is text interpolation using the "Mustache" syntax (double curly braces):
最基本的数据绑定形式是文本插值,它使用的是“Mustache”语法 (即双大括号):
template
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>The mustache tag will be replaced with the value of the msg property from the corresponding component instance. It will also be updated whenever the msg property changes.
双大括号标签会被替换为相应组件实例中 msg 属性的值。同时每次 msg 属性更改时它也会同步更新。
原始 HTML | Raw HTML
The double mustaches interpret the data as plain text, not HTML. In order to output real HTML, you will need to use the v-html directive:
双大括号会将数据解释为纯文本,而不是 HTML。若想插入 HTML,你需要使用 v-html 指令:
template
<p>Using text interpolation: {{ rawHtml }}</p>
<p>Using v-html directive: <span v-html="rawHtml"></span></p>Using text interpolation: <span style="color: red">This should be red.</span>
Using v-html directive: This should be red.
Here we're encountering something new. The v-html attribute you're seeing is called a directive. Directives are prefixed with v- to indicate that they are special attributes provided by Vue, and as you may have guessed, they apply special reactive behavior to the rendered DOM. Here, we're basically saying "keep this element's inner HTML up-to-date with the rawHtml property on the current active instance."
这里我们遇到了一个新的概念。这里看到的 v-html attribute 被称为一个指令。指令由 v- 作为前缀,表明它们是一些由 Vue 提供的特殊 attribute,你可能已经猜到了,它们将为渲染的 DOM 应用特殊的响应式行为。这里我们做的事情简单来说就是:在当前组件实例上,将此元素的 innerHTML 与 rawHtml 属性保持同步。
The contents of the span will be replaced with the value of the rawHtml property, interpreted as plain HTML - data bindings are ignored. Note that you cannot use v-html to compose template partials, because Vue is not a string-based templating engine. Instead, components are preferred as the fundamental unit for UI reuse and composition.
span 的内容将会被替换为 rawHtml 属性的值,插值为纯 HTML——数据绑定将会被忽略。注意,你不能使用 v-html 来拼接组合模板,因为 Vue 不是一个基于字符串的模板引擎。在使用 Vue 时,应当使用组件作为 UI 重用和组合的基本单元。
安全警告 | Security Warning
Dynamically rendering arbitrary HTML on your website can be very dangerous because it can easily lead to XSS vulnerabilities. Only use v-html on trusted content and never on user-provided content.
在网站上动态渲染任意 HTML 是非常危险的,因为这非常容易造成 XSS 漏洞。请仅在内容安全可信时再使用 v-html,并且永远不要使用用户提供的 HTML 内容。
Attribute 绑定 | Attribute Bindings
Mustaches cannot be used inside HTML attributes. Instead, use a v-bind directive:
双大括号不能在 HTML attributes 中使用。想要响应式地绑定一个 attribute,应该使用 v-bind 指令:
template
<div v-bind:id="dynamicId"></div>The v-bind directive instructs Vue to keep the element's id attribute in sync with the component's dynamicId property. If the bound value is null or undefined, then the attribute will be removed from the rendered element.
v-bind 指令指示 Vue 将元素的 id attribute 与组件的 dynamicId 属性保持一致。如果绑定的值是 null 或者 undefined,那么该 attribute 将会从渲染的元素上移除。
简写 | Shorthand
Because v-bind is so commonly used, it has a dedicated shorthand syntax:
因为 v-bind 非常常用,我们提供了特定的简写语法:
template
<div :id="dynamicId"></div>Attributes that start with : may look a bit different from normal HTML, but it is in fact a valid character for attribute names and all Vue-supported browsers can parse it correctly. In addition, they do not appear in the final rendered markup. The shorthand syntax is optional, but you will likely appreciate it when you learn more about its usage later.
开头为 : 的 attribute 可能和一般的 HTML attribute 看起来不太一样,但它的确是合法的 attribute 名称字符,并且所有支持 Vue 的浏览器都能正确解析它。此外,他们不会出现在最终渲染的 DOM 中。简写语法是可选的,但相信在你了解了它更多的用处后,你应该会更喜欢它。
For the rest of the guide, we will be using the shorthand syntax in code examples, as that's the most common usage for Vue developers.
接下来的指引中,我们都将在示例中使用简写语法,因为这是在实际开发中更常见的用法。
同名简写 | Same-name Shorthand
- 仅支持 3.4 版本及以上
If the attribute has the same name with the JavaScript value being bound, the syntax can be further shortened to omit the attribute value:
如果 attribute 的名称与绑定的 JavaScript 值的名称相同,那么可以进一步简化语法,省略 attribute 值:
template
<!-- same as :id="id" -->
<!-- 与 :id="id" 相同 -->
<div :id></div>
<!-- this also works -->
<!-- 这也同样有效 -->
<div v-bind:id></div>This is similar to the property shorthand syntax when declaring objects in JavaScript. Note this is a feature that is only available in Vue 3.4 and above.
这与在 JavaScript 中声明对象时使用的属性简写语法类似。请注意,这是一个只在 Vue 3.4 及以上版本中可用的特性。
布尔型 Attribute | Boolean Attributes
Boolean attributes are attributes that can indicate true / false values by their presence on an element. For example, disabled is one of the most commonly used boolean attributes.
布尔型 attribute 依据 true / false 值来决定 attribute 是否应该存在于该元素上。disabled 就是最常见的例子之一。
v-bind works a bit differently in this case:
v-bind 在这种场景下的行为略有不同:
template
<button :disabled="isButtonDisabled">Button</button>The disabled attribute will be included if isButtonDisabled has a truthy value. It will also be included if the value is an empty string, maintaining consistency with <button disabled="">. For other falsy values the attribute will be omitted.
当 isButtonDisabled 为真值或一个空字符串 (即 <button disabled="">) 时,元素会包含这个 disabled attribute。而当其为其他假值时 attribute 将被忽略。
动态绑定多个值 | Dynamically Binding Multiple Attributes
If you have a JavaScript object representing multiple attributes that looks like this:
如果你有像这样的一个包含多个 attribute 的 JavaScript 对象:
js
const objectOfAttrs = {
id: 'container',
class: 'wrapper',
style: 'background-color:green'
}You can bind them to a single element by using v-bind without an argument:
通过不带参数的 v-bind,你可以将它们绑定到单个元素上:
template
<div v-bind="objectOfAttrs"></div>使用 JavaScript 表达式 | Using JavaScript Expressions
So far we've only been binding to simple property keys in our templates. But Vue actually supports the full power of JavaScript expressions inside all data bindings:
至此,我们仅在模板中绑定了一些简单的属性名。但是 Vue 实际上在所有的数据绑定中都支持完整的 JavaScript 表达式:
template
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
<div :id="`list-${id}`"></div>These expressions will be evaluated as JavaScript in the data scope of the current component instance.
这些表达式都会被作为 JavaScript ,以当前组件实例为作用域解析执行。
In Vue templates, JavaScript expressions can be used in the following positions:
在 Vue 模板内,JavaScript 表达式可以被使用在如下场景上:
- Inside text interpolations (mustaches)
- 在文本插值中 (双大括号)
- In the attribute value of any Vue directives (special attributes that start with
v-) - 在任何 Vue 指令 (以
v-开头的特殊 attribute) attribute 的值中
仅支持表达式 | Expressions Only
Each binding can only contain one single expression. An expression is a piece of code that can be evaluated to a value. A simple check is whether it can be used after return.
每个绑定仅支持单一表达式,也就是一段能够被求值的 JavaScript 代码。一个简单的判断方法是是否可以合法地写在 return 后面。
Therefore, the following will NOT work:
因此,下面的例子都是无效的:
template
<!-- this is a statement, not an expression: -->
<!-- 这是一个语句,而非表达式 -->
{{ var a = 1 }}
<!-- flow control won't work either, use ternary expressions -->
<!-- 条件控制也不支持,请使用三元表达式 -->
{{ if (ok) { return message } }}调用函数 | Calling Functions
It is possible to call a component-exposed method inside a binding expression:
可以在绑定的表达式中使用一个组件暴露的方法:
template
<time :title="toTitleDate(date)" :datetime="date">
{{ formatDate(date) }}
</time>TIP
Functions called inside binding expressions will be called every time the component updates, so they should not have any side effects, such as changing data or triggering asynchronous operations.
绑定在表达式中的方法在组件每次更新时都会被重新调用,因此不应该产生任何副作用,比如改变数据或触发异步操作。
受限的全局访问 | Restricted Globals Access
Template expressions are sandboxed and only have access to a restricted list of globals. The list exposes commonly used built-in globals such as Math and Date.
模板中的表达式将被沙盒化,仅能够访问到有限的全局对象列表。该列表中会暴露常用的内置全局对象,比如 Math 和 Date。
Globals not explicitly included in the list, for example user-attached properties on window, will not be accessible in template expressions. You can, however, explicitly define additional globals for all Vue expressions by adding them to app.config.globalProperties.
没有显式包含在列表中的全局对象将不能在模板内表达式中访问,例如用户附加在 window 上的属性。然而,你也可以自行在 app.config.globalProperties 上显式地添加它们,供所有的 Vue 表达式使用。
指令 | Directives
Directives are special attributes with the v- prefix. Vue provides a number of built-in directives, including v-html and v-bind which we have introduced above.
指令是带有 v- 前缀的特殊 attribute。Vue 提供了许多内置指令,包括上面我们所介绍的 v-bind 和 v-html。
Directive attribute values are expected to be single JavaScript expressions (with the exception of v-for, v-on and v-slot, which will be discussed in their respective sections later). A directive's job is to reactively apply updates to the DOM when the value of its expression changes. Take v-if as an example:
指令 attribute 的期望值为一个 JavaScript 表达式 (除了少数几个例外,即之后要讨论到的 v-for、v-on 和 v-slot)。一个指令的任务是在其表达式的值变化时响应式地更新 DOM。以 v-if 为例:
template
<p v-if="seen">Now you see me</p>Here, the v-if directive would remove or insert the <p> element based on the truthiness of the value of the expression seen.
这里,v-if 指令会基于表达式 seen 的值的真假来移除/插入该 <p> 元素。
参数 | Arguments
Some directives can take an "argument", denoted by a colon after the directive name. For example, the v-bind directive is used to reactively update an HTML attribute:
某些指令会需要一个“参数”,在指令名后通过一个冒号隔开做标识。例如用 v-bind 指令来响应式地更新一个 HTML attribute:
template
<a v-bind:href="url"> ... </a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<!-- 简写 -->
<a :href="url"> ... </a>Here, href is the argument, which tells the v-bind directive to bind the element's href attribute to the value of the expression url. In the shorthand, everything before the argument (i.e., v-bind:) is condensed into a single character, :.
这里 href 就是一个参数,它告诉 v-bind 指令将表达式 url 的值绑定到元素的 href attribute 上。在简写中,参数前的一切 (例如 v-bind:) 都会被缩略为一个 : 字符。
Another example is the v-on directive, which listens to DOM events:
另一个例子是 v-on 指令,它将监听 DOM 事件:
template
<a v-on:click="doSomething"> ... </a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<!-- 简写 -->
<a @click="doSomething"> ... </a>Here, the argument is the event name to listen to: click. v-on has a corresponding shorthand, namely the @ character. We will talk about event handling in more detail too.
这里的参数是要监听的事件名称:click。v-on 有一个相应的缩写,即 @ 字符。我们之后也会讨论关于事件处理的更多细节。
动态参数 | Dynamic Arguments
It is also possible to use a JavaScript expression in a directive argument by wrapping it with square brackets:
同样在指令参数上也可以使用一个 JavaScript 表达式,需要包含在一对方括号内:
template
<!--
Note that there are some constraints to the argument expression,
as explained in the "Dynamic Argument Value Constraints" and "Dynamic Argument Syntax Constraints" sections below.
-->
<!--
注意,参数表达式有一些约束,
参见下面“动态参数值的限制”与“动态参数语法的限制”章节的解释
-->
<a v-bind:[attributeName]="url"> ... </a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<!-- 简写 -->
<a :[attributeName]="url"> ... </a>Here, attributeName will be dynamically evaluated as a JavaScript expression, and its evaluated value will be used as the final value for the argument. For example, if your component instance has a data property, attributeName, whose value is "href", then this binding will be equivalent to v-bind:href.
这里的 attributeName 会作为一个 JavaScript 表达式被动态执行,计算得到的值会被用作最终的参数。举例来说,如果你的组件实例有一个数据属性 attributeName,其值为 "href",那么这个绑定就等价于 v-bind:href。
Similarly, you can use dynamic arguments to bind a handler to a dynamic event name:
相似地,你还可以将一个函数绑定到动态的事件名称上:
template
<a v-on:[eventName]="doSomething"> ... </a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<!-- 简写 -->
<a @[eventName]="doSomething"> ... </a>In this example, when eventName's value is "focus", v-on:[eventName] will be equivalent to v-on:focus.
在此示例中,当 eventName 的值是 "focus" 时,v-on:[eventName] 就等价于 v-on:focus。
动态参数值的限制 | Dynamic Argument Value Constraints
Dynamic arguments are expected to evaluate to a string, with the exception of null. The special value null can be used to explicitly remove the binding. Any other non-string value will trigger a warning.
动态参数中表达式的值应当是一个字符串,或者是 null。特殊值 null 意为显式移除该绑定。其他非字符串的值会触发警告。
Dynamic Argument Syntax Constraints | 动态参数语法的限制
Dynamic argument expressions have some syntax constraints because certain characters, such as spaces and quotes, are invalid inside HTML attribute names. For example, the following is invalid:
动态参数表达式因为某些字符的缘故有一些语法限制,比如空格和引号,在 HTML attribute 名称中都是不合法的。例如下面的示例:
template
<!-- This will trigger a compiler warning. -->
<!-- 这会触发一个编译器警告 -->
<a :['foo' + bar]="value"> ... </a>If you need to pass a complex dynamic argument, it's probably better to use a computed property, which we will cover shortly.
如果你需要传入一个复杂的动态参数,我们推荐使用计算属性替换复杂的表达式,也是 Vue 最基础的概念之一,我们很快就会讲到。
When using in-DOM templates (templates directly written in an HTML file), you should also avoid naming keys with uppercase characters, as browsers will coerce attribute names into lowercase:
当使用 DOM 内嵌模板 (直接写在 HTML 文件里的模板) 时,我们需要避免在名称中使用大写字母,因为浏览器会强制将其转换为小写:
template
<a :[someAttr]="value"> ... </a>The above will be converted to :[someattr] in in-DOM templates. If your component has a someAttr property instead of someattr, your code won't work. Templates inside Single-File Components are not subject to this constraint.
上面的例子将会在 DOM 内嵌模板中被转换为 :[someattr]。如果你的组件拥有 “someAttr” 属性而非 “someattr”,这段代码将不会工作。单文件组件内的模板不受此限制。
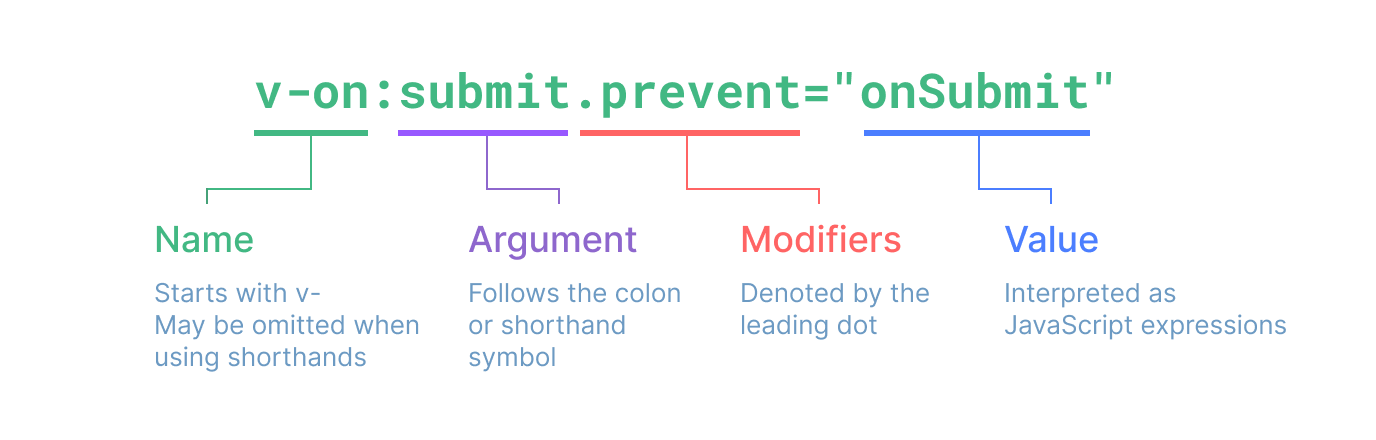
修饰符 | Modifiers
Modifiers are special postfixes denoted by a dot, which indicate that a directive should be bound in some special way. For example, the .prevent modifier tells the v-on directive to call event.preventDefault() on the triggered event:
修饰符是以点开头的特殊后缀,表明指令需要以一些特殊的方式被绑定。例如 .prevent 修饰符会告知 v-on 指令对触发的事件调用 event.preventDefault():
template
<form @submit.prevent="onSubmit">...</form>You'll see other examples of modifiers later, for v-on and for v-model, when we explore those features.
之后在讲到 v-on 和 v-model 的功能时,你将会看到其他修饰符的例子。
And finally, here's the full directive syntax visualized:
最后,在这里你可以直观地看到完整的指令语法: